Wednesday, February 19, 2025
Thursday, February 6, 2025
Thursday, August 17, 2023
Brian Cox Breaks Silence: "The Universe Existed Before Big Bang"
Modern Science explains the origin of the universe with the Big Bang Theory.
According to this theory, our world emerged from the explosion of singularity, a point in space-time where energy density and mass approach infinity, and all dimensions reach zero.
But Recently, Brian Cox has made a bold announcement stating that the universe has always existed and the Big Bang Theory is wrong.
Thursday, March 9, 2023
The most efficient Radionuclide Identifying Device (RID)
Detects and identifies nuclides in mixed, shielded and heavily masked configurations including Special Nuclear Material (SNM).
The DiscoveRAD is ultra-compact, rugged, sensitive, lightweight and.... is even game for a dip to 10 meters 1(IP68)!
Spectrometry at up to 1 million cps between 10 KeV to 1 MeV.
Wednesday, March 8, 2023
High Sensitivity Multifunction Compton Camera
|
Compton imaging exploits inelastic scattering, known as Compton scattering, using a Compton camera consisting of a scatterer detector in the front layer and an absorber detector in the back layer. Compton imaging can discriminate gamma rays over a wide energy range from several hundred keV to several MeV. Damavan Imaging was founded in 2014 to develop its 8 Temporal Imaging proprietary patents and software. In 2015 it won a big grant from the French Nuclear Waste Agency, ANDRA, to develop a Compton camera able to image low activity waste. In 2018 Damavan Imaging won a Horizon 2020 EU SME Award. Product Introduction: Temporal Imaging is a new concept for gamma ray imaging that uses both light and time distribution of each scintillation event to localize precisely each scintillation event in space (X,Y,Z), time (T) and energy (E). This new imaging concept allows an improvement on the voxel size for each scintillation event (1x1x2mm) on each of the two detector plates. It also allows a coincidence veto between the 2 Compton plates. Temporal δ Delta is the first device to use this new concept. It has an exceptional Signal/noise ratio thanks to the time veto between it’s 2 plates. The Temporal δ Delta V3 is equipped with a small spectroscopic CZT detector and also enable isotope identification, simple dosimetry and 4 Pi source detection. Temporal δ is the best Compton imager (400 KeV - 3000 KeV), excellent spectrometer (50 KeV - 3000 KeV), stable photon counter with dose estimation. |
Tuesday, October 11, 2022
10 μm-thick four-quadrant transmissive silicon photodiodes for beam position monitor application: electrical characterization and gamma irradiation effects
Abstract:
Silicon photodiodes are very useful devices as X-ray beam monitors in synchrotron radiation beamlines. Owing to Si absorption, devices thinner than 10 µm are needed to achieve transmission over 90% for energies above 10 keV.
In this work, new segmented four-quadrant diodes for beam alignment purposes are fabricated on both ultrathin (10 µm-thick) and bulk silicon substrates. Four-quadrant diodes implementing different design parameters as well as auxiliary test structures (single diodes and MOS capacitors) are studied. An extensive electrical characterization, including current-voltage (I-V) and capacitance-voltage (C-V) techniques, is carried out on non-irradiated and gamma-irradiated devices up to 100 Mrad doses. Special attention is devoted to the study of radiation-induced charge build-up in diode interquadrant isolation dielectric, as well as its impact on device interquadrant resistance.
Finally, the devices have been characterized with an 8 keV laboratory X-ray source at 108 ph/s and in BL13-XALOC ALBA Synchrotron beamline with 1011 ph/s and energies from 6 to 16 keV. Sensitivity, spatial resolution and uniformity of the devices have been evaluated
Thursday, September 1, 2022
A1427 KIT Low Noise Fast Current Preamplifier & Discriminator
A1427 Kit configuration is also available. It includes the A1427 and the A1428 assembled together, both for fission chambers and for proton recoil detectors.
Features:
- Fast non-inverting preamplifier, negative output (EOUT)
- Input impedance: 50 Ω AC coupled
- Output high impedance (EOUT)
- Bipolar output high impedance (FOUT)
- Test input (TEST IN) impedance: 50 Ω, negative polarity
- FOUT/DET IN gain (FOUT negative lobe):
- FC version: 700÷2500
- PR version: 500÷1500
- FOUT/TEST IN gain: 1/100 of DET IN gain
- Output noise (peak to peak) < 40 mV
- Up to 3 kV detector bias voltage (HV IN)
- Rbias: 200 kΩ
Wednesday, February 16, 2022
New Portable Device for Automated Radon Detection
The Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), through the Institute of Microelectronics of Barcelona (IMB-CNM-CSIC), has collaborated in the design and development of a prototype for the detection of radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can be found in the interior spaces of buildings. It consists of a small device that connects to a wireless network and automatically monitors radon levels in its environment in buildings. This detection system contains a silicon sensor manufactured in the Clean Room of the IMB-CNM-CSIC.
The prototype, still in the standardization phase, is the result of the CARE project, an initiative that has been led by the company Alibava Systems and has had the participation of two public research centers, the IMB-CNM-CSIC and the Instituto Galego de Física de Altas Enerxías (IGFAE) of the Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, which has been responsible for carrying out the calibration and validation tests, both in its experimental facilities and in real environments. CARE also involves three companies, ATI Sistemas SL, Radiansa Consulting SL, Sensing & Control Systems SL.
Tuesday, October 5, 2021
Compact Tracking Telescope for High Energy Particles
OVERVIEW
The ALIBAVA Telescope has been successfully operated at the DESY and CERN-SPS beam lines.
The telescope consists of at least three planes (stations). The stations use ALIBAVA daughter boards to take the tracking information from two 90 degrees-turned strip sensors for XY positioning. The stations act as reference frame and allow precise track reconstruction. Each daughter connects to an ALIBAVA motherboard to process the information and they to a unique master board that synchronizes and controls the whole system. The system is triggered by two scintillators located at both ends.
Several devices can be tested simultaneously. Analysis of charge collection, cluster width, efficiency, resolution, time profile and other parameters of the devices under test with the software provided.
The telescope provides accurate particle tracking and hit point projection on device under test.
FEATURES
This product is sold under license of Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and University of Valencia (Spain)
- Sensor: Microstrip Silicon, P‐on‐N silicon.
- Sensor size: 10x10 mm2
- Thickness: 300 μm
- Read-out channels: 128
- Pitch: 80 μm
- Spatial resolution: < 10 μm
- Chip BEETLE (technology from CERN/LHC)
- Clock speed: 40 MHz
- Dynamic range: 4 MIP
- Synchronous external trigger. Trigger boards available.
- Analysis software for Windows, Linux, Mac.
- Station dimensions: 100x80 mm2
- Mother and Master board dimensions: 247x172x32 mm3
- Voltage supply: +5 V
- Mechanical structure and cooling available
Tuesday, September 7, 2021
Hands-on Educational Tool for Physics
Thursday, June 10, 2021
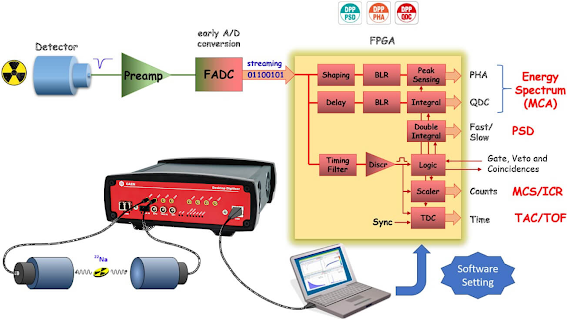
CAEN Digitizer Whitepaper
- More density, faster sampling rate, higher resolution for higher performances
- Increased communication readout through 1/10 Gb Ethernet, USB 3.0 (yet keeping proprietary CONET)
- Easier multi-board synchronization (clock and timing distribution)
- Increase of acquisition memory buffer size: from SSRAM to DDR4 (=> from MBs to GBs)
- Single FPGA (Xilinx Zynq US+ ) architecture => more resources for DPP algorithms and support for “Open FPGA”
- Embedded quad-core ARM (Linux) => middleware, web interface. Possibility to run user Data Processing SW
Friday, January 22, 2021
CAEN x1081 Programmable Logic Units
Coincidence, Trigger Logic, Counter, Pulse Generator and more
>>> Click to start video <<<
Wednesday, December 2, 2020
Didactic Kits for University of Fribourg
During Q1/2012 they will be receiving two new Educational Kits & Experiments for training students with state-of-the-art didactic tools from CAEN, world leader in nuclear and particle physics instrumentation.
SP5700-EasyPET in this tutorial, is a simple, user friendly and portable didactic PET system developed for high-level education, which allows exploring the physical and technological principles of the conventional human PET scanners, using the same basic detectors of state-of- the-art systems. The Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanner is the state-of-the-art medical imaging system, capable of providing detailed functional information of physiological processes inside the human body. Functional imaging has a great impact in cancer diagnostics, monitoring of therapy effects and cancer drug development. The underlying principle to PET systems is the detection of high energy radiation emitted from a chemical marker, a molecule labelled with a radioisotope, administered to a patient. The radioisotope emits positrons which, after annihilating with atomic electrons, result in the isotropic emission of two photons back to back with an energy of 511 keV. The two photons are detected by a ring of detectors, which allows a pair of them to detect two back to back photons in any direction.
Friday, October 9, 2020
Black Holes Matter

Roger Penrose for linking black hole formation to relativity; Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez for discovery of supermassive object.
Monday, June 8, 2020
Radiation detection for Gamma Spectroscopy and/or Neutron-Gamma Discrimination
- PMT replacement in physics experiment
- Laboratory R&D on SiPM technology
- Portable Gamma-Spectroscopy Industrial process monitoring
- Environmental Monitoring
- Handheld border control against illicit traffic of radioactive material
- Neutron detection experiments
- Vehicle/personnel check-point portals
Thursday, October 10, 2019
2019 Nobel Prize in Physics
Exoplanets, or extra solar planets, are planets beyond our solar system. This 4 minutes National Geographic video explains their discovery and significance.
In 1995, Professor Michel Mayor and his doctoral student Didier Queloz discovered 51 Pegasi B, a planet orbiting a sun-like star beyond our solar system. Their discovery created great interest in the field and research since then has led to the discovery of around 4,000 exoplanets, some of which might support life. Proxima Centauri b, the closest potentially habitable exoplanet, is 40 trillion km (4.2 light years) from earth.
A 4th physicist, John Goodenough, shared the Chemistry award with Stanley Whittingham and Akira Yoshino for the development of lithium-ion batteries.
Thursday, October 3, 2019
Build your Muons telescope!
New Educational Kit
- Cosmic muons detection
- Coincidence (single, double and triple)
- Zenit angle dependence of the muon flux
- Cosmic shower detection
- Based on SiPM detectors and plastic scintillating tiles.
- Up to 3 scintillating tiles management
- Flexible system geometry
- No need of software interface
- Embedded E-Ink Display
- SD card to download data
Tuesday, August 20, 2019
Experiment to Detect Dark Energy Turns Up Nothing
The accelerated expansion of the universe motivates a wide class of scalar field theories that modify general relativity (GR) on large scales. Such theories require a screening mechanism to suppress the new force in regions where the weak field limit of GR has been experimentally tested. The scientists used atom interferometry to measure the acceleration of an atom toward a macroscopic test mass inside a high vacuum chamber, where new forces can be unscreened. The measurement show no evidence of new forces, a result that places stringent bounds on chameleon and symmetron theories of modified gravity.
Click for more